
316 stainless steel is suitable for use in applications such as chemical processing equipment, food processing equipment, and medical devices where corrosion resistance is required Conclusion: ApplicationsĤ46 stainless steel is suitable for use in applications such as boiler tubes, heat exchangers, and exhaust systems where corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength are required. Chromium helps to protect the metal from scaling at high temperatures by forming a thin oxide layer on the surface of the metal. The increased scaling resistance of 446 stainless steel over 316 stainless steel is due to the higher chromium content. Molybdenum is a metal that helps to resist corrosion by forming a protective oxide layer on the surface of the metal. The increased corrosion resistance of 446 stainless steel over 316 stainless steel is due to the addition of molybdenum. Let’s take a closer look at their respective compositions and properties so you can make the best choice for your application. While both 446 and 316 stainless steels share some characteristics, they have several key differences that set them apart from one another. Difference Between 446 and 316 Stainless Steel The higher levels of nickel give this grade excellent corrosion resistance against reducing acids like hydrochloric acid, while the higher molybdenum content gives it superior corrosion resistance against chloride ion solutions like those found in saltwater environments, making it ideal for applications such as marine hardware or food processing equipment that will be exposed to salt water conditions on a regular basis. 316 Stainless Steelģ16-grade stainless steel is composed primarily of iron and chromium but also contains trace amounts of nickel, molybdenum, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur titanium in addition to other elements. Additionally, due to its high chromium content and low carbon content, 446-grade stainless steel has excellent formability properties allowing it to be easily formed into complex shapes without sacrificing strength or durability. This makes it particularly well-suited for applications where oxidation resistance is important such as chemical processing equipment or automotive exhaust components.

The high levels of chromium give 446-grade stainless steel excellent corrosion resistance against oxidizing acids like nitric acid and sulfuric acid. It also contains trace amounts of nickel, manganese, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, and titanium, in addition to other elements. 446 Stainless SteelĤ46 stainless steel is composed primarily of iron, chromium, and carbon. In this blog post, we’ll explore two common grades of stainless steel-446 and 316-and discuss the differences between them so you can make an informed decision about which one is right for your needs. But not all stainless steel is created equal-there are a variety of different grades available, each with its own unique properties.
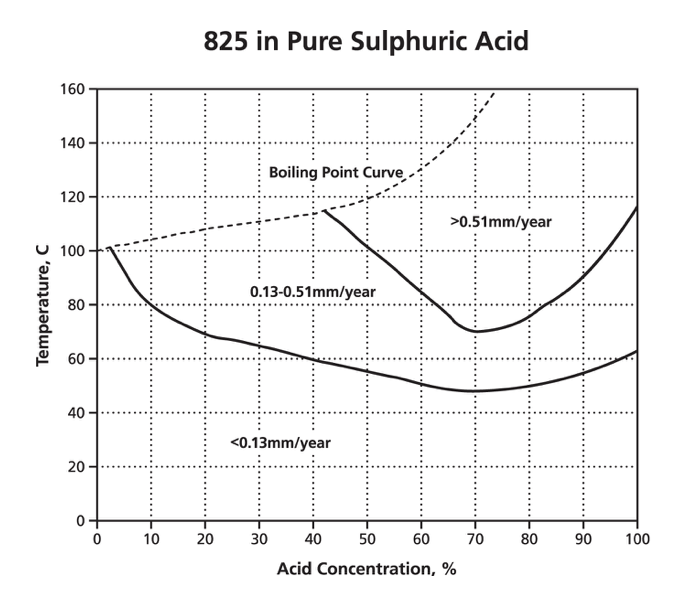
It’s resistant to corrosion, heat, and chemicals, making it one of the most versatile metals out there. Stainless steel is an incredibly useful material.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
